中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 121-132.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00148
• • 上一篇
葛健辉1,2( ), 刘冰1(
), 刘冰1( ), 徐宇杰1,2, 孙爱军1,2,3, 汪克奇1,2, 李冬雪1,2, 赵晖1
), 徐宇杰1,2, 孙爱军1,2,3, 汪克奇1,2, 李冬雪1,2, 赵晖1
收稿日期:2023-08-31
修回日期:2023-10-21
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通讯作者:
刘冰
作者简介:刘冰(E-mail: liubing2014@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Jianhui Ge1,2( ), Bing Liu1(
), Bing Liu1( ), Yujie Xu1,2, Aijun Sun1,2,3, Keqi Wang1,2, Dongxue Li1,2, hui Zhao1
), Yujie Xu1,2, Aijun Sun1,2,3, Keqi Wang1,2, Dongxue Li1,2, hui Zhao1
Received:2023-08-31
Revised:2023-10-21
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Bing Liu
摘要:
黄河首曲是世界高海拔地区生物多样性丰富和生态变化敏感的地区,其环境演变过程如何响应区域气候变化具有重要的科学意义。针对该区末次冰消期以来气候环境重建结果的分歧,以目前已发表的多载体记录为基础,独立集成区域气候变化的框架性过程和地表环境演变历史,进而探讨两者的相互关系。结果表明:(1)该区在13~6 ka气温和湿度持续增加,10~6 ka为气候最优期,6 ka以后气温和湿度逐渐下降,气候变冷变干。(2)18~11 ka地表过程以河湖相过程为主,风沙活动非常弱;11~8 ka河湖沉积过程减弱,风沙活动增强;8~3 ka古土壤大规模发育;3 ka以来广泛发育草甸土。(3)区域地表环境变化过程与气候变化之间存在非同步变化,6 ka以前气候变化对区域地表过程呈正向驱动,6 ka以后对区域地表过程呈负向驱动。基于现代和晚全新世草甸土壤粒度的比较,发现草甸土壤的发育是气候变冷变干背景下风成物质不断加积的产物,进一步暗示区域土壤发育与气候变化间的复杂关系。
中图分类号:
葛健辉, 刘冰, 徐宇杰, 孙爱军, 汪克奇, 李冬雪, 赵晖. 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域气候变化与地表过程相互关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 121-132.
Jianhui Ge, Bing Liu, Yujie Xu, Aijun Sun, Keqi Wang, Dongxue Li, hui Zhao. Interrelationships between climate change and surface processes in the First Meander of the Yellow River since the Last Deglaciation[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 121-132.
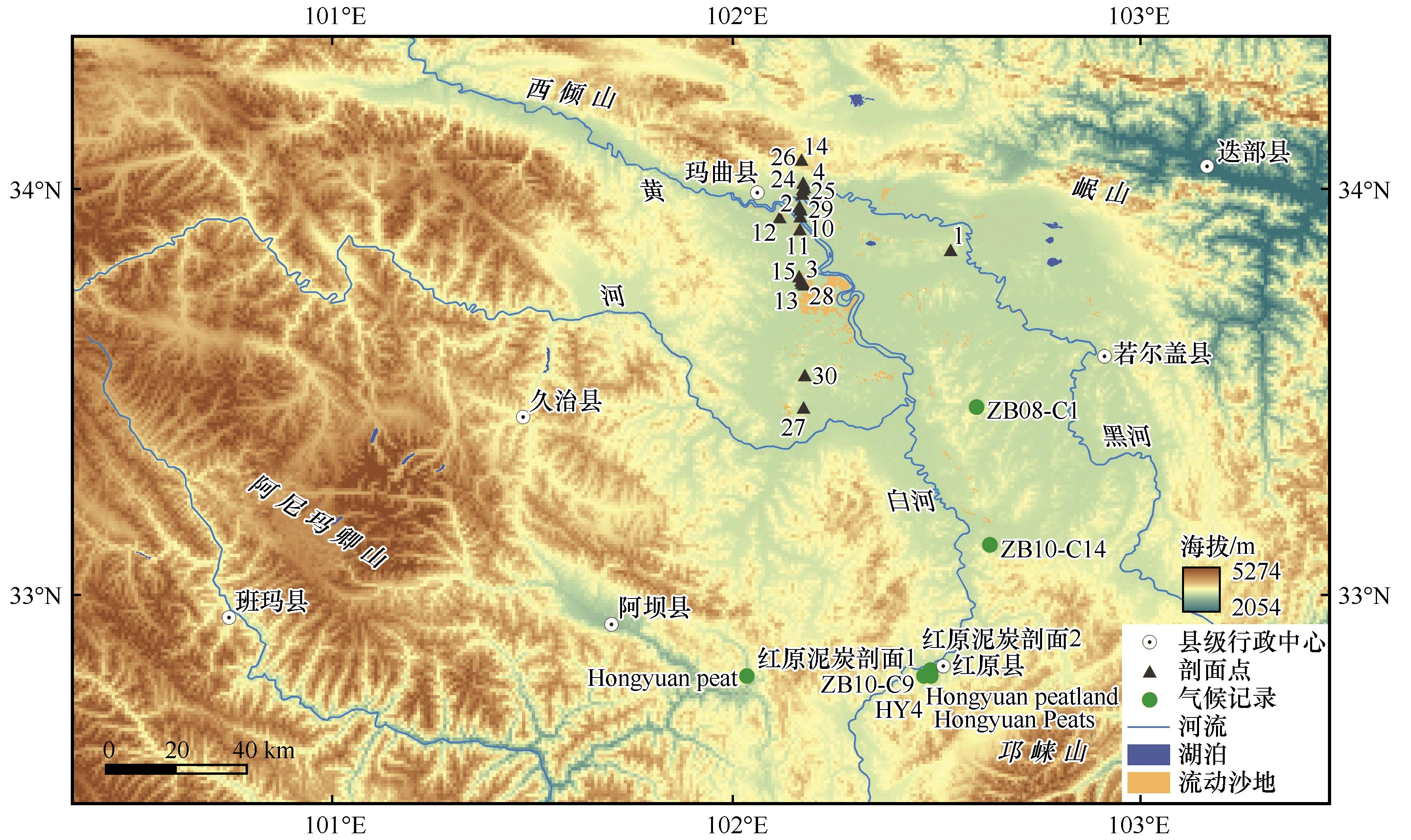
图1 黄河首曲流域古气候环境数据空间分布(剖面编号对应表2序号)注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:川S【2021】00050号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.1 Spatial distribution map of paleoclimate environmental data in the First Meander of the Yellow River (numbers correspond to serial numbers in Table 2)
| 编号 | 剖面名称 | 纬度 (°N) | 经度 (°E) | 测年 方式 | 时间范围 /ka BP | 年代 数 | 分辨率 /a | 代用 指标 | 指标 意义 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tw1 | ZB08-C1 | 33.45 | 102.63 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 8 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| Tw2 | ZB10-C9 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 15 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| Tw3 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 18 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| T1 | ZB08-C1 | 33.45 | 102.63 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 8 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T2 | ZB10-C9 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 15 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T3 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 18 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T4 | HY4 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.0~0 | 8 | ~100 | BrGDGTs | MAT | Yan等[ |
| T5 | Hongyuan Peats | 32.77 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.0~0 | 11 | ~100 | GDGTs | MAT | Zheng等[ |
| P1 | Hongyuan peat | 32.77 | 102.05 | AMS14C | 12.0~0 | 15 | ~30 | 木里苔草碳同位素 | 夏季风 | Hong等[ |
| P2 | Hongyuan peatland | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.5~0 | 32 | ~25 | 冷杉花粉 | 夏季风 | Zhou等[ |
| P3 | 红原泥炭剖面1 | 32.77 | 102.50 | AMS14C | 12.0~0 | 15 | ~30 | 腐殖化度 | 湿度 | 王华等[ |
| P4 | 红原泥炭剖面2 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.5~0 | 11 | ~15-20 | 灰度 | 夏季风 | 于学峰等[ |
| P5 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 10.5~0 | 18 | ~60 | 针叶林相似性得分 | 湿度 | 孙晓红等[ |
表1 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域古气候记录
Table 1 Records of paleoclimate evolution since the Last Deglaciation in the First Meander of Yellow River
| 编号 | 剖面名称 | 纬度 (°N) | 经度 (°E) | 测年 方式 | 时间范围 /ka BP | 年代 数 | 分辨率 /a | 代用 指标 | 指标 意义 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tw1 | ZB08-C1 | 33.45 | 102.63 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 8 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| Tw2 | ZB10-C9 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 15 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| Tw3 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 18 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MTwa | Liang等[ |
| T1 | ZB08-C1 | 33.45 | 102.63 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 8 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T2 | ZB10-C9 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 15 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T3 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 11.0~0 | 18 | ~60 | 孢粉 | MAT | Liang等[ |
| T4 | HY4 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.0~0 | 8 | ~100 | BrGDGTs | MAT | Yan等[ |
| T5 | Hongyuan Peats | 32.77 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.0~0 | 11 | ~100 | GDGTs | MAT | Zheng等[ |
| P1 | Hongyuan peat | 32.77 | 102.05 | AMS14C | 12.0~0 | 15 | ~30 | 木里苔草碳同位素 | 夏季风 | Hong等[ |
| P2 | Hongyuan peatland | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 13.5~0 | 32 | ~25 | 冷杉花粉 | 夏季风 | Zhou等[ |
| P3 | 红原泥炭剖面1 | 32.77 | 102.50 | AMS14C | 12.0~0 | 15 | ~30 | 腐殖化度 | 湿度 | 王华等[ |
| P4 | 红原泥炭剖面2 | 32.78 | 102.52 | AMS14C | 11.5~0 | 11 | ~15-20 | 灰度 | 夏季风 | 于学峰等[ |
| P5 | ZB10-C14 | 33.10 | 102.67 | AMS14C | 10.5~0 | 18 | ~60 | 针叶林相似性得分 | 湿度 | 孙晓红等[ |
| 序号 | 类型 | 剖面 名称 | 纬度 (°N) | 经度 (°E) | 时间范围 /ka BP | 测年 手段 | 年代 数 | 代用指标 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section1 | 33.85 | 102.57 | 10~3.5 | OSL | 2 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 2 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section2 | 33.93 | 102.13 | 3~0.5 | OSL | 5 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 3 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section3 | 33.78 | 102.18 | 1~0 | OSL | 3 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 4 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MQQ | 33.96 | 102.08 | 10~0 | AMS14C | 6 | 粒度、磁化率 | Yang等[ |
| 5 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.5 | — | — | — | 14C | 1 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 6 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.6 | — | — | 3.5~0.5 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 7 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.9 | — | — | — | 14C | 1 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 8 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.10 | — | — | 1.5~0.5 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 9 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.21 | — | — | 1.5~0 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 10 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MO | 33.90 | 102.16 | 6~0 | 14C | 5 | 地化元素 | 胡梦珺等[ |
| 11 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | OL | 33.94 | 102.02 | 5.5~0 | 14C | 5 | 地化元素 | 杨爱丽[ |
| 12 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | LQXR | 33.95 | 102.07 | 7.5~1 | OSL | 4 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 13 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | LQXA | 33.77 | 102.21 | 4~0.5 | OSL | 7 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 14 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | XCC | 34.08 | 102.58 | 4.5~1.5 | OSL | 5 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素 | 柴佳楠等[ |
| 15 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | XM | 33.7 | 102.53 | 16~1 | AMS14C | 5 | 粒度、磁化率 | 綦琳等[ |
| 16 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | OQC | — | — | 18~0 | OSL | 5 | 粒度 | 王娜等[ |
| 17 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | WQD | — | — | 18~0 | OSL, AMS14C | 6 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 18 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | AB | — | — | 1.5~0.5 | AMS14C | 2 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 19 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | EF | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 20 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MN | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 21 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | GH | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 22 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | IJ | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 23 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | PQ | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 24 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | TWR | 33.99 | 101.92 | 13.5~8.5 | OSL | 4 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 陈莹璐等[ |
| 25 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | DEQ-E | 34.00 | 101.90 | 18~1 | OSL | 7 | 粒度、磁化率 | 肖奇立等[ |
| 26 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | ZHK | 34.02 | 101.89 | 14~0 | OSL, AMS14C | 5 | 粒度、磁化率 | Jia等[ |
| 27 | 河湖相沉积 | WDT | 33.45 | 102.45 | 5~0 | OSL | 3 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素 | 柴佳楠等[ |
| 28 | 河湖相沉积 | LQ | 33.76 | 102.24 | 9.5~0 | OSL, 14C | 6 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 左海玲[ |
| 29 | 河湖相沉积 | DEQ | 34.01 | 101.88 | 18~0 | OSL | 4 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 戎晓庆[ |
| 30 | 河湖相沉积 | JYM | 33.53 | 102.48 | 18~0 | OSL | 14 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 戎晓庆[ |
| 31 | 河湖相沉积 | 剖面P.7 | — | — | 12~2 | AMS14C | 3 | — | 徐先英等[ |
表2 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域古环境/地表过程记录
Table 2 Record of paleoenvironmental/surface processes in the First Meander of the Yellow River since the Last Deglaciation
| 序号 | 类型 | 剖面 名称 | 纬度 (°N) | 经度 (°E) | 时间范围 /ka BP | 测年 手段 | 年代 数 | 代用指标 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section1 | 33.85 | 102.57 | 10~3.5 | OSL | 2 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 2 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section2 | 33.93 | 102.13 | 3~0.5 | OSL | 5 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 3 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | section3 | 33.78 | 102.18 | 1~0 | OSL | 3 | 粒度、总有机碳 | Hu等[ |
| 4 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MQQ | 33.96 | 102.08 | 10~0 | AMS14C | 6 | 粒度、磁化率 | Yang等[ |
| 5 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.5 | — | — | — | 14C | 1 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 6 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.6 | — | — | 3.5~0.5 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 7 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.9 | — | — | — | 14C | 1 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 8 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.10 | — | — | 1.5~0.5 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 9 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | 剖面P.21 | — | — | 1.5~0 | 14C | 2 | — | 徐先英等[ |
| 10 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MO | 33.90 | 102.16 | 6~0 | 14C | 5 | 地化元素 | 胡梦珺等[ |
| 11 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | OL | 33.94 | 102.02 | 5.5~0 | 14C | 5 | 地化元素 | 杨爱丽[ |
| 12 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | LQXR | 33.95 | 102.07 | 7.5~1 | OSL | 4 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 13 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | LQXA | 33.77 | 102.21 | 4~0.5 | OSL | 7 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 14 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | XCC | 34.08 | 102.58 | 4.5~1.5 | OSL | 5 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素 | 柴佳楠等[ |
| 15 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | XM | 33.7 | 102.53 | 16~1 | AMS14C | 5 | 粒度、磁化率 | 綦琳等[ |
| 16 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | OQC | — | — | 18~0 | OSL | 5 | 粒度 | 王娜等[ |
| 17 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | WQD | — | — | 18~0 | OSL, AMS14C | 6 | 粒度 | 周家和等[ |
| 18 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | AB | — | — | 1.5~0.5 | AMS14C | 2 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 19 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | EF | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 20 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | MN | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 21 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | GH | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 22 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | IJ | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 23 | 风成砂-古土壤序列 | PQ | — | — | — | AMS14C | 1 | 粒度、重矿物 | 邹学勇等[ |
| 24 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | TWR | 33.99 | 101.92 | 13.5~8.5 | OSL | 4 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 陈莹璐等[ |
| 25 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | DEQ-E | 34.00 | 101.90 | 18~1 | OSL | 7 | 粒度、磁化率 | 肖奇立等[ |
| 26 | 黄土-古土壤序列 | ZHK | 34.02 | 101.89 | 14~0 | OSL, AMS14C | 5 | 粒度、磁化率 | Jia等[ |
| 27 | 河湖相沉积 | WDT | 33.45 | 102.45 | 5~0 | OSL | 3 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素 | 柴佳楠等[ |
| 28 | 河湖相沉积 | LQ | 33.76 | 102.24 | 9.5~0 | OSL, 14C | 6 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 左海玲[ |
| 29 | 河湖相沉积 | DEQ | 34.01 | 101.88 | 18~0 | OSL | 4 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 戎晓庆[ |
| 30 | 河湖相沉积 | JYM | 33.53 | 102.48 | 18~0 | OSL | 14 | 粒度、磁化率、地化元素等 | 戎晓庆[ |
| 31 | 河湖相沉积 | 剖面P.7 | — | — | 12~2 | AMS14C | 3 | — | 徐先英等[ |
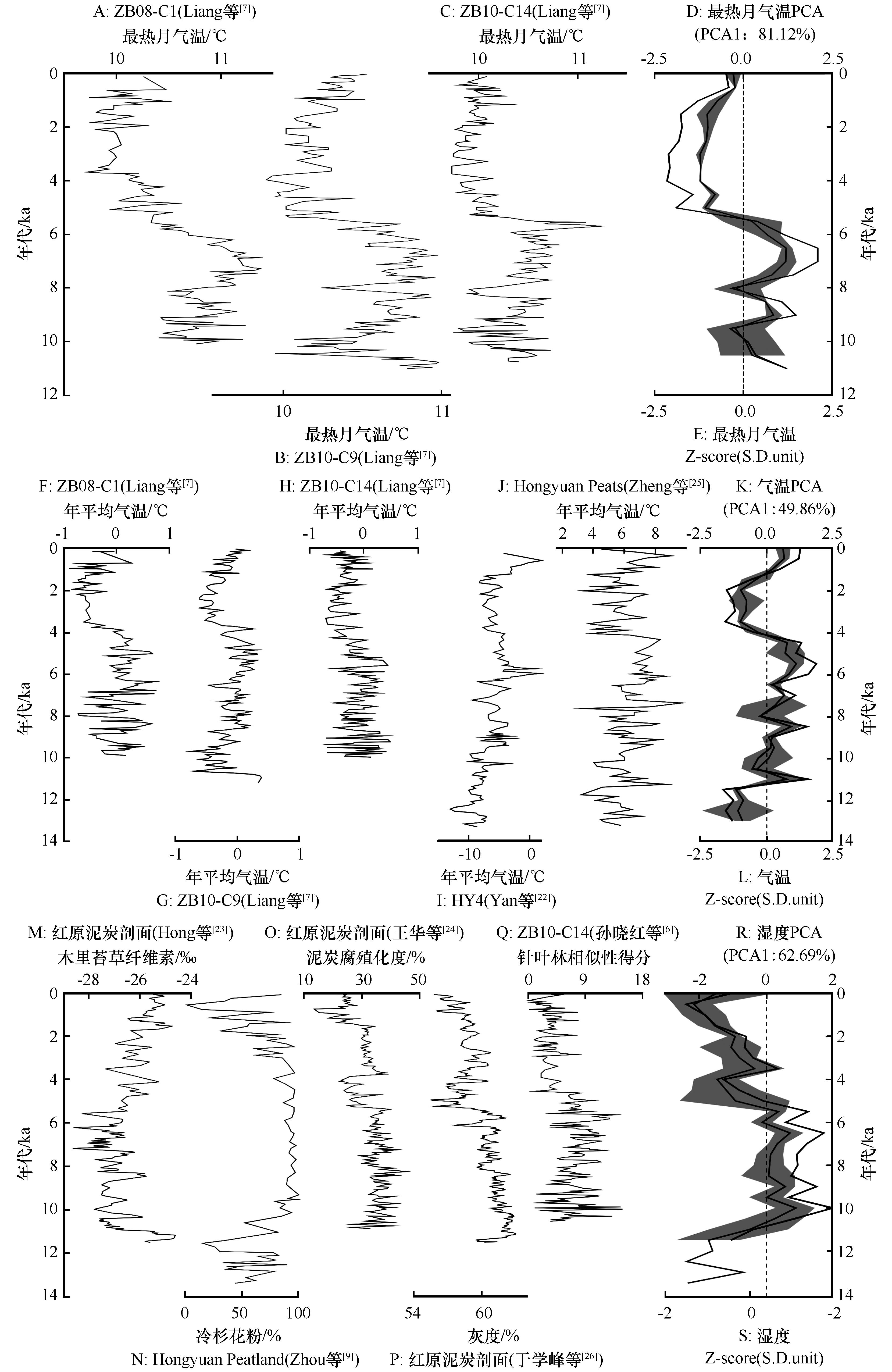
图2 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域古气候变化的综合集成注:PCA为主成分分析;Z-score(S.D.unit)为算术平均;阴影部分为算术平均计算对应误差
Fig.2 Comprehensive integration of paleoclimate records in the First Meander of the Yellow River since the Last Delaciation
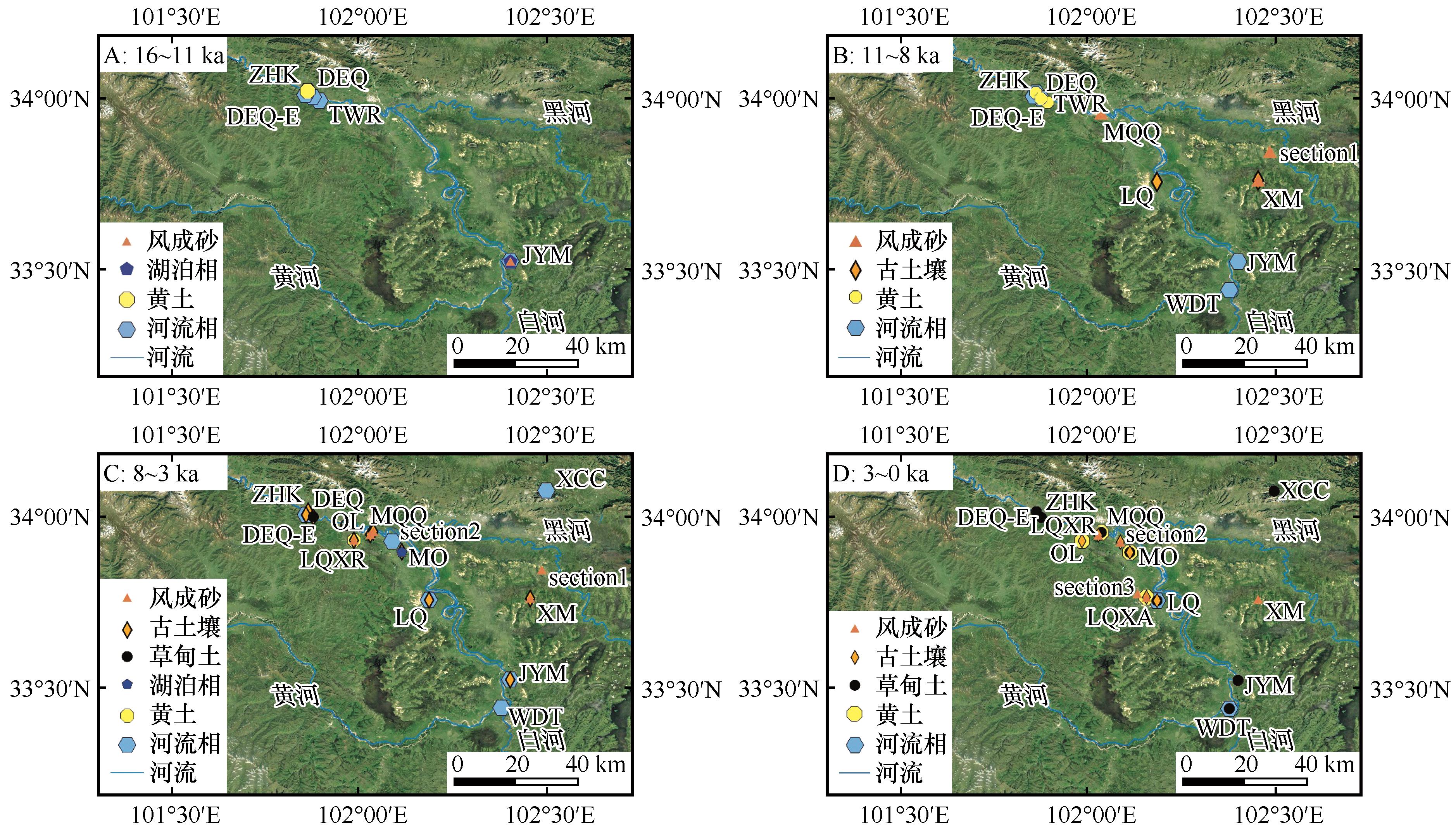
图4 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域环境演变的时空分布
Fig.4 Spatial and temporal distribution of environmental evolution in the First Meander of the Yellow River since the Last Deglaciation
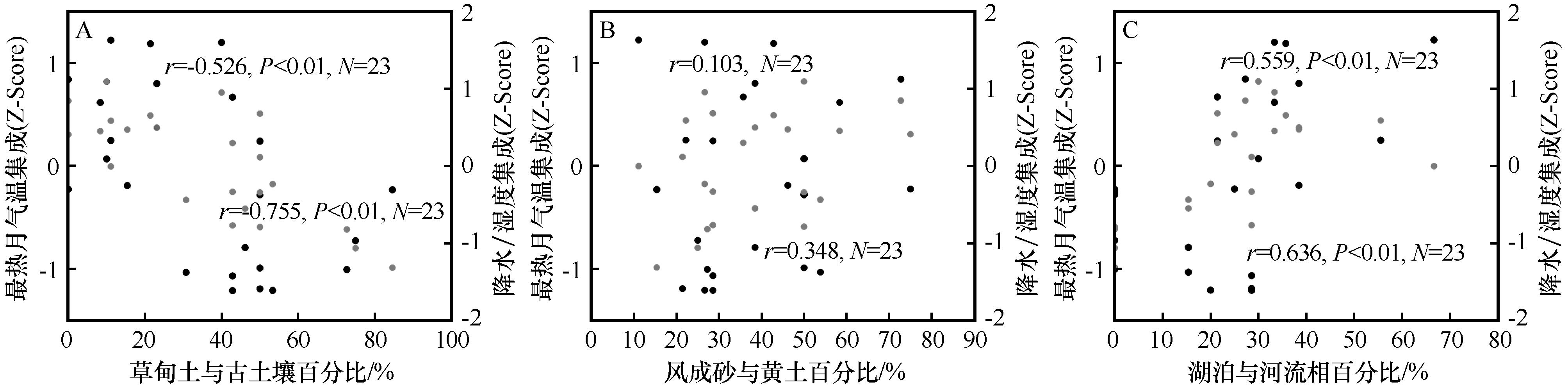
图5 11 ka以来黄河首曲流域环境演变与气候因素的相互关系注:灰色点为降水/湿度集成
Fig.5 The relationship between surface processes and climate factors in the First Meander of Yellow River since 11 ka
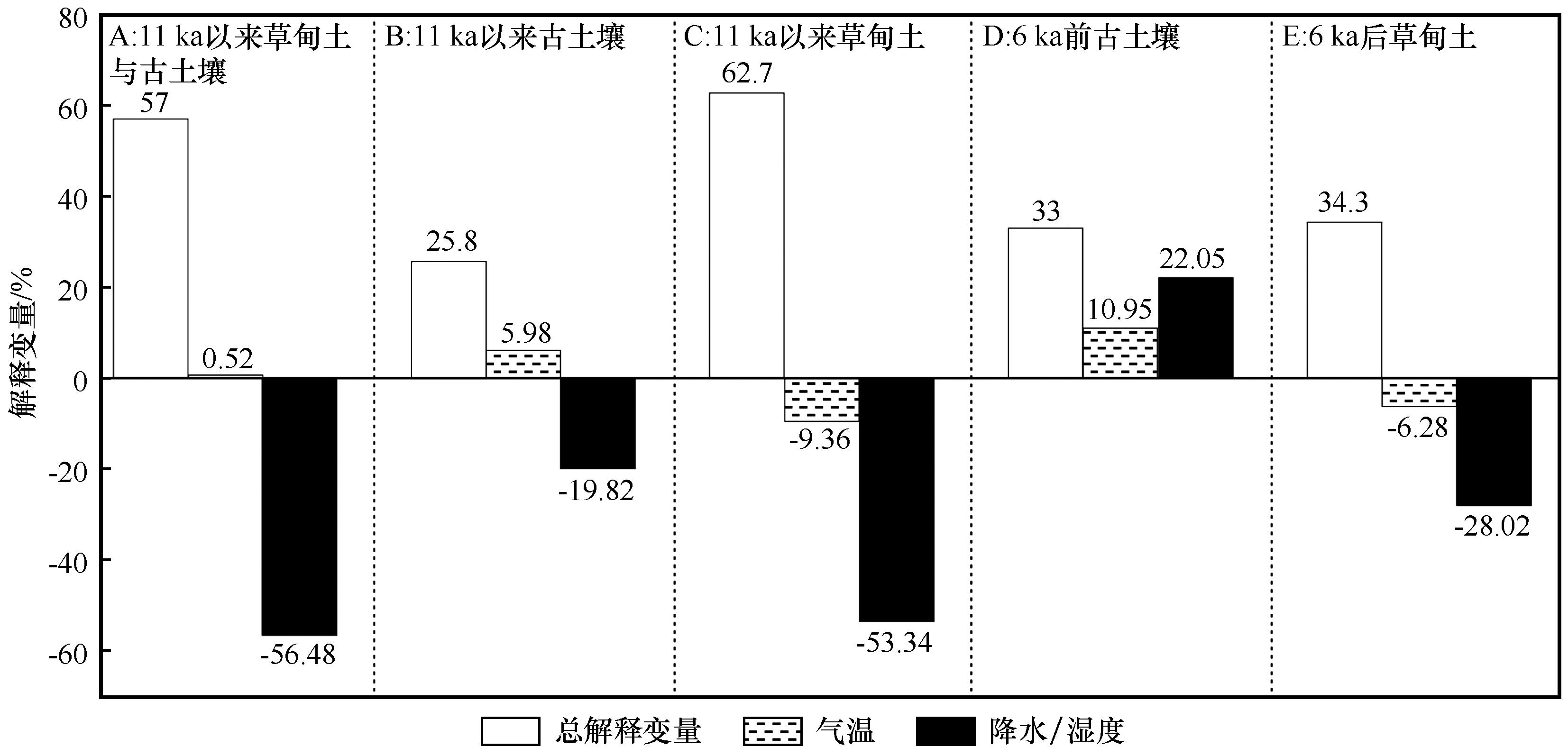
图6 气温和降水/湿度对不同时段草甸土与古土壤发育的贡献
Fig.6 Contribution of temperature and precipitation/humidity to the development of meadow soil and paleosol at different time periods
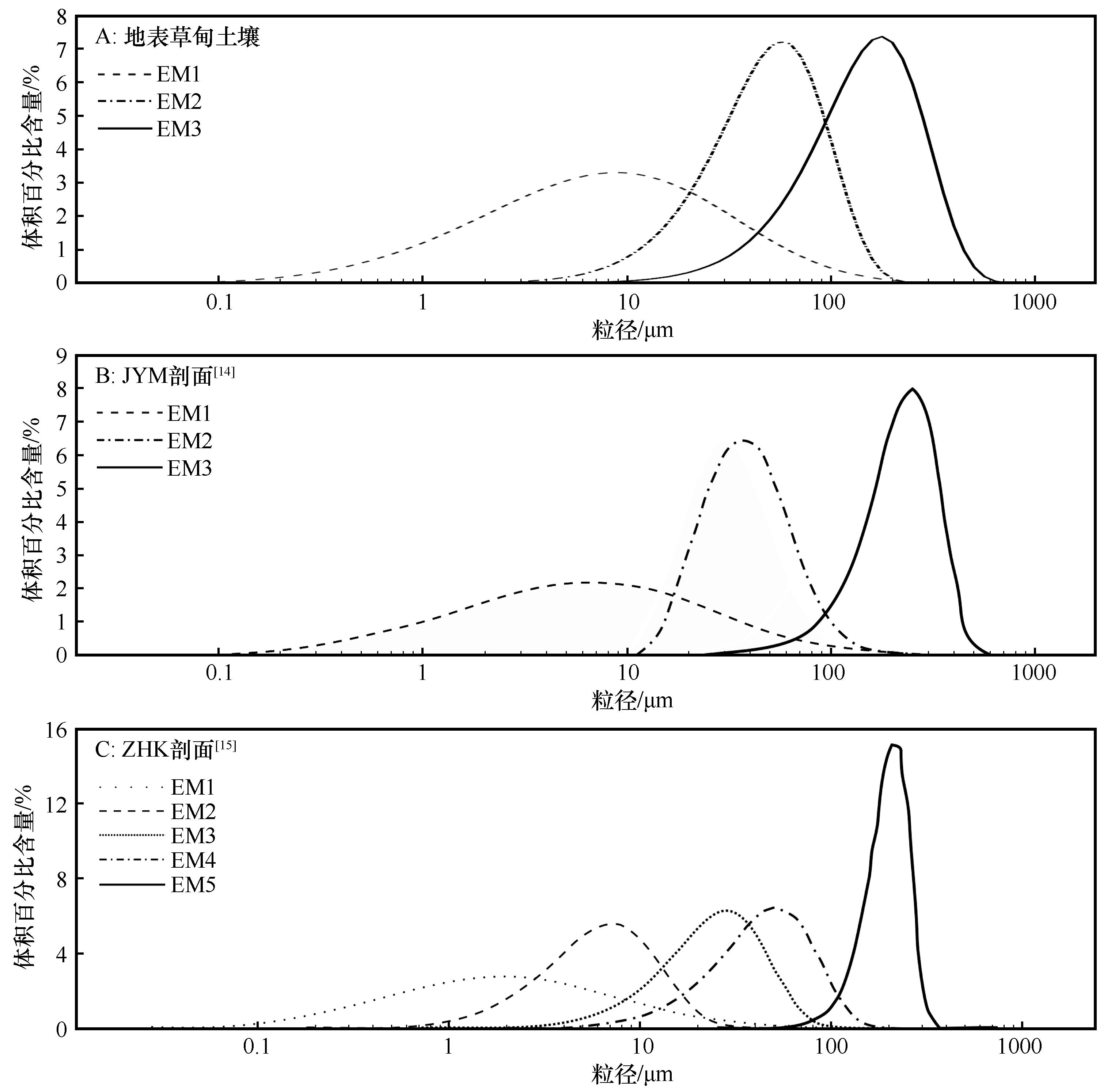
图7 黄河首曲流域地表草甸土壤及草甸土剖面各端元粒度自然分布频率曲线
Fig.7 Natural distribution frequency curve of surface meadow soil and end-element grain size of meadow soil profile in the First Meander of Yellow River and its surrounding area
| 1 | 计伟,刘海江,高吉喜,等.黄河流域生态质量时空变化分析[J].环境科学研究,2021,34(7):1700-1709. |
| 2 | 黄春长.若尔盖盆地河流古洪水沉积及其对黄河水系演变问题的启示[J].地理学报,2021,76(3):612-625. |
| 3 | 王娜,查小春,黄春长,等.青藏高原东部黄河切开若尔盖湖盆的沉积证据与年代研究[J].地理科学进展,2022,41(8):1453-1466. |
| 4 | 任继周,林慧龙.江河源区草地生态建设构想[J].草业学报,2005,14(2):1-8. |
| 5 | 王辉,任继周,袁宏波.黄河源区天然草地沙化机理分析研究[J].草业学报,2006,15(6):19-25. |
| 6 | 孙晓红,赵艳,李泉.青藏高原东部若尔盖盆地全新世泥炭地发育和植被变化[J].中国科学:地球科学,2017,47(9):1097-1109. |
| 7 | Liang C, Zhao Y, Qin F,et al.Pollen-based Holocene quantitative temperature reconstruction on the eastern Tibetan Plateau using a comprehensive method framework[J].Science China Earth Sciences,2020,63(8):1144-1160. |
| 8 | Zhao Y, Yu Z C, Zhao W W.Holocene vegetation and climate histories in the eastern Tibetan Plateau:controls by insolation-driven temperature or monsoon-derived precipitation changes?[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2011,30(9/10):1173-1184. |
| 9 | Zhou W J, Yu S Y, Burr G S,et al.Postglacial changes in the Asian summer monsoon system:a pollen record from the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Boreas,2010,39:528-539. |
| 10 | Hu G Y, Yu L P, Dong Z B,et al.Holocene aeolian activity in the Zoige Basin,northeastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Catena,2018,160:321-328. |
| 11 | 周家和,周亚利,黄春长,等.全新世若尔盖盆地沙丘光释光测年与风沙活动研究[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(5):1349-1362. |
| 12 | Wu D, Zhang C B, Wang T,et al.East-west asymmetry in the distribution of rainfall in the Chinese Loess Plateau during the Holocene[J].Catena,2021,207:105626. |
| 13 | 左海玲.郎曲剖面记录的全新世以来玛曲高原的沉积环境演变[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2016. |
| 14 | 戎晓庆.青藏高原东部若尔盖盆地甲央玛剖面OSL测年及其意义[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2020. |
| 15 | Jia Y N, Zhang Y Z, Huang C C,et al.Late Pleistocene-Holocene aeolian loess-paleosol sections in the Yellow River source area on the northeast Tibetan Plateau:chronostratigraphy,sediment provenance,and implications for paleoclimate reconstruction[J].Catena,2022,208:105777. |
| 16 | 胡梦珺,杨爱丽,张文丽.常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(2):313-321. |
| 17 | 柴佳楠,查小春,黄春长,等.若尔盖盆地黄河辖曼段河岸沉积物成因判别[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(5):600-607. |
| 18 | 柴佳楠.若尔盖盆地一级河流阶地沉积物测年及阶地形成过程研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2021. |
| 19 | Wang N, Zha X C, Huang C C,et al.Age and causes of the Yellow River dissecting the Zoige Basin in the eastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2023,857:159481. |
| 20 | 徐先英,唐进年,金红喜.黄河首曲高寒草地沙化防治研究[M].兰州:甘肃科学技术出版社,2019:1-52. |
| 21 | 肖奇立,陈豆,张玉柱,等.黄河源玛曲段末次冰消期以来古洪水事件与冻融褶皱现象研究[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(4):1010-1026. |
| 22 | Yan T L, Zhao C, Yan H,et al.Elevational differences in Holocene thermal maximum revealed by quantitative temperature reconstructions at ~30° N on eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2021,570:110364. |
| 23 | Hong Y T, Hong B, Lin Q H,et al.Correlation between Indian Ocean summer monsoon and North Atlantic climate during the Holocene[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2003,211(3/4):371-380. |
| 24 | 王华,洪业汤,朱咏煊,等.青藏高原泥炭腐殖化度的古气候意义[J].科学通报,2004,49(7):686-691. |
| 25 | Zheng Y, Li Q, Wang Z,et al.Peatland GDGT records of Holocene climatic and biogeochemical responses to the Asian Monsoon[J].Organic Geochemistry,2015,87:86-95. |
| 26 | 于学峰,周卫健, Franzen L G,等.青藏高原东部全新世冬夏季风变化的高分辨率泥炭记录[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2006,36(2):182-187. |
| 27 | Yang S L, Liu X J, Cheng T,et al.Stepwise weakening of aeolian activities during the Holocene in the Gannan region,Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:677-686. |
| 28 | 胡梦珺,左海玲,潘宁惠,等.中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的化学风化过程演变[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):623-635. |
| 29 | 杨爱丽.地化学元素揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的成壤环境演变[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2015. |
| 30 | 綦琳,王燕,蔡遥,等.若尔盖风成砂-古土壤序列的古气候与古环境记录研究[J].地质力学学报,2020,26(2):244-251. |
| 31 | 周家和,周亚利,黄春长,等.若尔盖黄河唐克段河岸沉积序列测年及地表过程变化[J].冰川冻土,2022,44(4):1188-1202. |
| 32 | 邹学勇,王贵勇.黄河上游玛曲地区晚全新世沙漠化[J].中国沙漠,1995,15(1):65-70. |
| 33 | 陈莹璐,黄春长,张玉柱,等.黄河源区玛曲段末次冰消期古洪水事件及其光释光测年研究[J].冰川冻土,2017,39(3):549-562. |
| 34 | 陈莹璐.黄河玛曲段和汝河遂平段古洪水事件年代及其气候背景对比研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2018. |
| 35 | Xu Z W, Mason J A, Xu C,et al.Critical transitions in Chinese dunes during the past 12,000 years[J].Science Advances,2020,6(9):8020. |
| 36 | 张小梅,靳鹤龄,刘冰.末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境变化[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(5):81-93. |
| 37 | 徐宇杰,刘冰,孙爱军,等.古尔班通古特沙漠及周边区域全新世环境演变研究进展[J].干旱区地理,2023,46(4):550-562. |
| 38 | Liu B, Zhao H, Li S H,et al.Asynchronous paleosol development during the past 20 ka in response to climate change across the dune fields of the Asian summer monsoonal boundary,northern China[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2022,234:104232. |
| 39 | Liu B, Zhao H, Yang F,et al.A new aeolian activity proxy based on analysis of the grain size characteristics of surface soils across the Tengger Desert,northwest China,and its application to a Quaternary aeolian succession[J].Paleogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Paleoecology,2023,622:111594. |
| 40 | Zhang J, E C Y, Wu C Y,et al.An alpine meadow soil chronology based on OSL and radiocarbon dating,Qinghai Lake,northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary International,2020,562:35-45. |
| 41 | Qiang M, Jin Y, Liu X,et al.Late Pleistocene and Holocene aeolian sedimentation in Gonghe Basin,northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau:variability,processes,and climatic implications [J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,132:57-73. |
| 42 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D,et al.Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments,and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J].Sedimentary Geology,2002,152(3/4):263-277. |
| 43 | Liu X X, Sun Y B, Vandenberghe J,et al.Palaeoenvironmental implication of grain-size compositions of terrace deposits on the western Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Aeolian Research,2018,32:202-209. |
| 44 | Liu Y M, Liu X X, Sun Y.QGrain:an open-source and easy-to-use software for the comprehensive analysis of grain size distributions[J].Sedimentary Geology,2021,423:105980. |
| 45 | Peng J, Wang X L, Yin G M,et al.Accumulation of aeolian sediments around the Tengger Desert during the late Quaternary and its implications on interpreting chronostratigraphic records from drylands in north China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2022,275:107288. |
| 46 | Peng J, Zhao H, Dong Z B,et al.Numerical methodologies and tools for efficient and flexible unmixing of single-sample grain-size distributions:application to late Quaternary aeolian sediments from the desert-loess transition zone of the Tengger Desert[J].Sedimentary Geology,2022,438:106211. |
| 47 | 王兆夺,黄春长,周亚利,等.若尔盖盆地黄河第一湾河岸沉积地层序列及其成因研究[J].冰川冻土,2022,44(4):1175-1187. |
| 48 | Zhang J, E C Y, Yang F,et al.OSL ages and pedogenic mode of Kobresia mattic epipedon on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Catena,2023,223:106912. |
| 49 | Lin Y C, Feng J L.Aeolian dust contribution to the formation of alpine soils at Amdo (Northern Tibetan Plateau)[J].Geoderma,2015,259/260:104-115. |
| [1] | 李庆, 周娜, 王盛, 李童洲, 王仁德, 王金凤. 气候变化和人类活动对土壤风蚀影响的定量评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 178-188. |
| [2] | 冯筱, 屈建军, 丁新辉, 田琴, 范庆斌. 沙漠化逆转过程中榆林市植被净初级生产力时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 22-32. |
| [3] | 赵延卓, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 呼伦贝尔沙地风成砂-古土壤剖面记录的全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 85-96. |
| [4] | 路建兵, 鞠珂, 廖伟斌. 2000—2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. |
| [5] | 尤其, 许宝荣, 邹松兵, 秦艺豪, 王铎, 于冬. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被-气候响应关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 274-287. |
| [6] | 王耀宗, 岳新斌, 谢家丽, 刘志鹏, 马媛, 王亚晖, 宫燕. 2000—2020年宁夏河东沙区沙漠化演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 31-40. |
| [7] | 梁鹏飞, 辛惠娟, 李宗省, 南富森, 唐彪, 张文豹. 基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 210-219. |
| [8] | 段然, 李宗杰, 王昱, 刘晓颖, 桂娟, 梁鹏飞, 李玉辰, 薛健, 刘梦晴, 徐斌. 石羊河流域径流变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 57-68. |
| [9] | 韩子言, 蒙吉军, 邹易, 朱利凯. 1982—2017年黑河流域植被指数动态及其对气候变化与生态建设工程的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [10] | 辛春明, 何明珠, 李承义, 张力斌, 李新荣. 荒漠土壤氧化亚氮排放及其驱动因素研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 184-194. |
| [11] | 孙红, 段霁芸, 刘雨洁, 冉瑞兰, 李晓凤, 赵鹏善. 气候变化背景下沙蓬属( Agriophyllum )物种潜在地理分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 255-263. |
| [12] | 杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 刘怡婷, 李嘉宁, 杨天宇. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3 、S3 黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [13] | 和海秀, 付爱红, 王川. 塔城地区西北部低山草甸植被指数变化及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 187-196. |
| [14] | 秦豪君, 杨晓军, 马莉, 王一丞, 傅朝, 张君霞, 陆正奇. 2000—2020年中国西北地区区域性沙尘暴特征及成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [15] | 柳欣滢, 金明, 杨帆, 马亚鹏, 刘慧, 孙小云, 夏敦胜. 毛乌素沙地东缘中全新世以来环境变化及其对文明演化的影响初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
